Picup your order for free
Provide a more affordable shopping experience

LED technology has ushered in a wave of fresh innovations and a greater array of choices within the lighting industry. Manufacturers continually introduce new products, expanding the options available to consumers.
The primary advantage of these fixtures lies in their flexibility. On-site customization of these fixtures is easily achievable, which can streamline the design process and result in both time and cost savings.
Today, we'll delve into their operational principles, examine the pros and cons, and provide guidance on selecting the optimal options.
Should you require a refresher on lighting terminology or an introduction to the basics, here are invaluable definitions pertaining to color and wattage-selectable LEDs:
Color Temperature - This gauge denotes the degree of yellow or blue in the light emitted by a bulb. Warm light sources, such as incandescent bulbs, possess a low color temperature (2200-3000K), appearing more yellow or orange. Cool light sources, like certain HID or fluorescent lamps, boast a high color temperature (>4000K) and tend to appear bluer.
Color Rendering Index (CRI) - While the CRI cannot be altered with selectable fixtures, it is a critical term to comprehend when procuring lighting. CRI predicts how accurately the light output will depict colors. This metric ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating truer color representation under the light.
Wattage - This measures the power consumption of a lighting fixture, quantified in watts. In general, LEDs consume fewer watts than traditional incandescent or fluorescent fixtures. Typically, higher wattage translates to greater brightness.
Rather than ordering fixtures with predetermined color temperatures or wattages, color and wattage-selectable LEDs enable adjustments to be made on-site. Most of these fixtures offer adjustability via a switch or dial.
The following are examples of color and wattage selection switches from various manufacturers, which may be situated on the exterior of a replacement bulb, within a fixture or retrofit kit, or on the outer surface of a fixture housing.
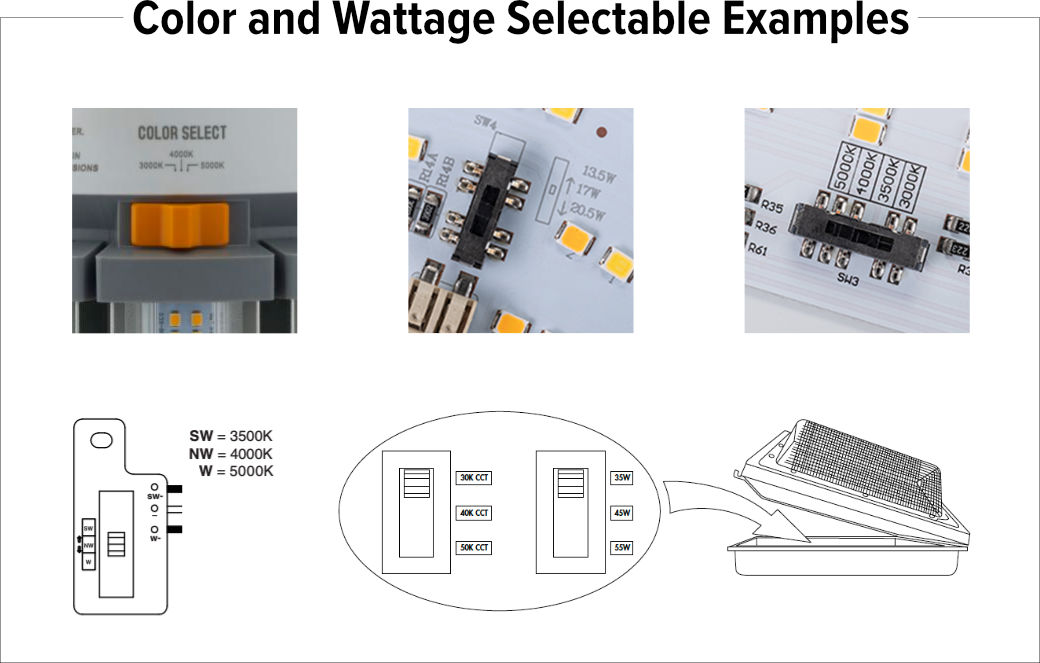
It is advisable to choose the color temperature and wattage prior to the full installation of the fixture. While adjustments can be made subsequently if necessary, it might entail labor to access or remove fixtures for modifying the settings.
When selecting the color temperature, your focus is on determining the warmth or coolness of the light's appearance. Choosing wattage equates to selecting the lumens (brightness) of the fixture. Making these selections in the field allows you to evaluate how the light actually complements the space.
The Benefits of Color and Wattage-Selectable Lighting Products
These products offer advantages to both consumers and manufacturers. Consumers gain enhanced flexibility, while manufacturers can reduce the variety of products they need to produce.
While color and wattage-selectable LEDs represent a technological leap forward, they may not be suitable for every application. Here's an overview of the pros and cons:
Leave a comment